يتطور عصر "أمن النماذج" إلى "أمن البنية التحتية". بينما أمضت الصناعة عام 2025 في القلق بشأن "الحقن الموجه"، إلا أن الخراب الحقيقي قد وصل إلى طبقة التنسيق.
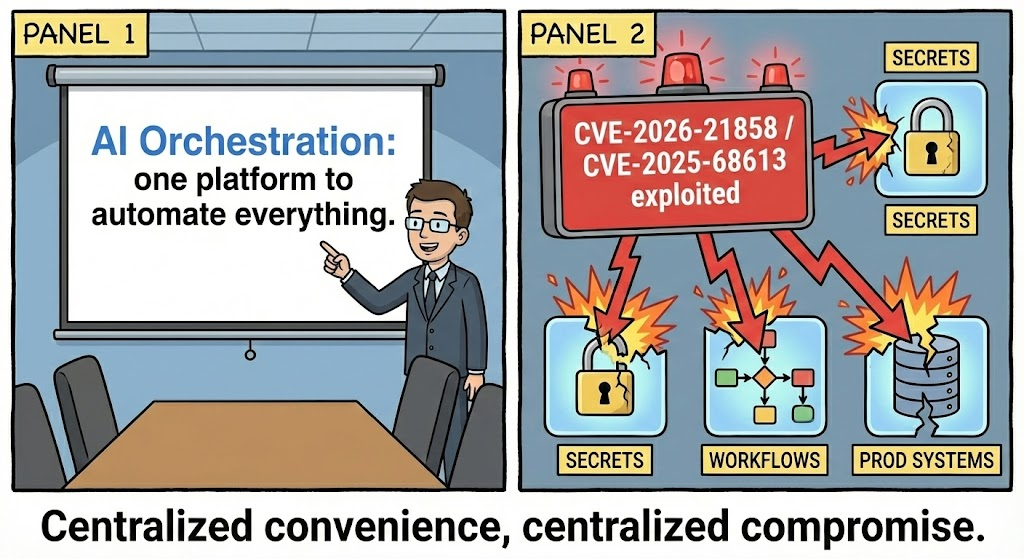
افتتح شهر يناير 2026 بكشف كارثي لمجتمع هندسة الذكاء الاصطناعي: CVE-2026-21858هي ثغرة أمنية غير مصادق عليها في نظام CVSS 10.0 لتنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية عن بُعد (RCE) في ن8 ن. يأتي ذلك بعد أقل من شهر من الكشف عن CVE-2025-68613RCE المصادق عليه في نفس النظام الأساسي.
بالنسبة لمهندسي الأمن والفريق الأحمر، فإن n8n ليست مجرد "أداة"؛ فهي العمود الفقري لآلاف وكلاء الذكاء الاصطناعي المستقلين، حيث تربط بين LLMs (OpenAI، وAnthropic) بقواعد البيانات الداخلية وواجهات برمجة التطبيقات. إن المساس بـ n8n يعني المساس بسلسلة توريد الذكاء الاصطناعي بأكملها.
تفكك هذه المقالة سلاسل استغلال الثغرات الأمنية لكلا الثغرتين، وتحلل الأسباب الجذرية، وتوفر مسارات علاجية قابلة للتنفيذ.
كابوس "Ni8mare": تفكيك فيروس CVE-2026-21858 (RCE غير المصادق عليه)
الخطورة: حرجة (CVSS 10.0)
الناقل الشبكة / غير مصادق عليه
التأثير: الاستحواذ الكامل على الخادم
مدبلج "ني8ماري" من قبل باحثين في Cyera، يمثل CVE-2026-21858 أسوأ سيناريو للبنية التحتية للذكاء الاصطناعي: الاستيلاء غير المصادق عليه دون نقرات.
السبب الجذري: الارتباك في نوع المحتوى
تكمن الثغرة في منطق معالجة خطاف الويب الخاص ب n8n وكيفية معالجته لطلبات HTTP الواردة. يستخدم n8n برنامجًا وسيطًا لتحليل البيانات الواردة بناءً على نوع المحتوى الرأس.
في الإصدارات الضعيفة (قبل الإصدار 1.121.0)، فشل التطبيق في فرض العلاقة بين نوع المحتوى ومنطق التحليل الفعلي المستخدم لإدارة الحالة الداخلية.
يمكن للمهاجم أن يرسل طلب HTTP مصمم خصيصاً لهذا الغرض:
- يعلن عن حميدة
نوع المحتوى(على سبيل المثال,تطبيق/جسون) لتجاوز عمليات التحقق الأولية لجدار الحماية (WAF). - يتلاعب ببنية الجسم لخداع المُحلِّل الداخلي لتجاوز
req.bodyالكائن. - حقن معلمات تكوين خبيثة يثق بها التطبيق بشكل أعمى.
مسار الاستغلال
يسمح هذا الخلل الخطير للمهاجمين "بالتشويش" على الخادم لقبول مسار تحميل ملف يقوم بالكتابة فوق ملفات التكوين الداخلية، مثل التكوين أو قاعدة البيانات.sqlite.
وبمجرد الكتابة فوق التهيئة، يمكن للمهاجم:
- إعادة تعيين المصادقة: الكتابة فوق بيانات اعتماد المستخدم المسؤول.
- استخراج الأسرار: اقرأ
.envأو ملفات التهيئة التي تحتوي على مفاتيح واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لخدمات الجهات الخارجية (AWS، OpenAI، Stripe). - تنفيذ الكود: استخدم عقدة "تنفيذ الأوامر" التي يمكن الوصول إليها الآن لتوليد غلاف عكسي.
جافا سكريبت
'/// كود زائف يوضح الخلل المنطقي // منطق قابل للخطأ: الوثوق في مدخلات المستخدم لمعالجة الملفات دون إجراء عمليات تحقق صارمة من النوع
التطبيق.post('/webhook/:id', (req, res) => { // يفترض المحلل أنه إذا كانت 'files' موجودة في النص الأساسي، فهذا يعني أنه تحميل صحيح // لكن يمكن أن يحاكي نص JSON مصمم بصياغة هذه البنية إذا (req.body.files && req.body.files.config_override) { // CRITICAL: الكتابة فوق الحالة الداخلية استنادًا إلى مدخلات غير مصادق عليها internalState.updateConfig(req.body.files.config_override.path)؛ } executeWorkflow(معرف req.params.id); });`
نظرًا لأن n8n غالبًا ما يتم تشغيله بامتيازات عالية لتنفيذ مهام النظام، فإن عملية إعادة الإنفاذ هذه تمنح فعليًا وصولًا على مستوى الجذر إلى الحاوية المضيفة.
السلائف CVE-2025-68613 (مصادقة RCE)
الخطورة: حرجة (CVSS 9.9.9)
الناقل الشبكة / مصادق عليه (امتيازات منخفضة)
قبل "Ni8mare" غير المصادق عليه، كان هناك CVE-2025-68613. على الرغم من أنها أقل خطورة بسبب شرط المصادقة، إلا أنها سلطت الضوء على هشاشة تقييم التعبير في سير عمل الذكاء الاصطناعي.
السبب الجذري حقن التعبير
يسمح n8n للمستخدمين بكتابة تعبيرات JavaScript لتحويل البيانات بين العقد. تسمح هذه الثغرة (التي تؤثر على الإصدارات السابقة للإصدار 1.122.0) للمهاجمين الذين لديهم وصول "عضو" أو وصول منخفض المستوى بالخروج من صندوق الحماية الخاص بالتعبيرات.
عن طريق صياغة سير عمل خبيث مع حمولة JavaScript محددة داخل حقل تعبير (على سبيل المثال، داخل حقل مجموعة node)، يمكن للمهاجمين الوصول إلى Node.js العملية الكائن.
سيناريو الهجوم
- الوصول: يحصل المهاجم على حق الوصول إلى حساب منخفض الامتيازات (على سبيل المثال، من خلال رابط دعوة مسرب أو كلمة مرور ضعيفة).
- الحمولة: إنشاء سير عمل باستخدام
الوظيفةأوالكودالعقدة. - الهروب: الاستخدام
إرجاع global.process.mainModule.require('child_process').execSync('id');لتجاوز القيود. - التنفيذ: في اللحظة التي يتم فيها "اختبار" سير العمل أو "تنشيطه"، يتم تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية على الخادم.
مقارنة تقنية: مشهد التهديدات في عام 2026 مقابل 2025
| الميزة | CVE-2026-21858 ("Ni8mare") | CVE-2025-68613 |
|---|---|---|
| المصادقة | لا شيء (غير مصادق عليه) | مطلوب (خاص منخفض) |
| درجة CVSS | 10.0 (حرج) | 9.9 (حرج) |
| السبب الجذري | الارتباك في نوع المحتوى/محلل المحتوى | الهروب من وضع الحماية/حقن التعبير |
| ناقل الهجوم | نقاط نهاية خطاف الويب | واجهة مستخدم محرر سير العمل |
| الهدف الأساسي | مستمعو خطاف الويب الموجه للجمهور | بيئات التطوير الداخلية/المشتركة |
أهمية ذلك بالنسبة لأمن الذكاء الاصطناعي
هذه الثغرات ليست مجرد "ثغرات في الخوادم"؛ فهي سلسلة التوريد بالذكاء الاصطناعي الخروقات
- التسمم بـ RAG يمكن للمهاجم الذي يتحكم في n8n اعتراض المستندات التي تتدفق إلى قاعدة بيانات Vector الخاصة بك، وحقن أبواب خلفية أو بيانات خاطئة في قاعدة معارف شركتك.
- اختطاف العملاء يمكن إعادة برمجة العوامل المستقلة المبنية على نظام n8n لاستخراج البيانات أو شن هجمات على أنظمة داخلية أخرى.
- سرقة أوراق الاعتماد تعمل n8n بمثابة "مخزن مفاتيح" لمزودي خدمة LLM. تكشف عملية RCE واحدة عن
OPENAI_API_KEY,أنثروبيك_بابي_مفتاحوبيانات اعتماد قاعدة البيانات.
التخفيف والمعالجة
مطلوب اتخاذ إجراء فوري:
- التصحيح فوراً: ترقية n8n إلى الإصدار 1.122.0 أو أعلى على الفور. يعمل هذا على تصحيح كل من CVEs.
- عزل الشبكة: لا تعرض أبدًا واجهة لوحة تحكم n8n (المنفذ 5678) مباشرة إلى الإنترنت العام. استخدم شبكة افتراضية خاصة أو وكيل عكسي مع مصادقة صارمة (على سبيل المثال، Cloudflare Access، Authelia).
- تعقيم خطاطيف الويب: إذا كان لا بد من عرض خطافات الويب، فتأكد من أنها خلف بوابة واجهة برمجة التطبيقات التي تتحقق من صحة مخطط الطلب قبل وصوله إلى مثيل n8n.
التحقق الآلي: النهج التوكيلي
في عالم 2026 سريع الحركة، لا يكفي الاعتماد على إدارة التصحيح اليدوي أو الاختبارات الخماسية السنوية. حيث تظهر الثغرات مثل CVE-2026-21858 بين عشية وضحاها ويتم تسليحها في غضون ساعات.
هذا هو المكان بنليجنت يغير النموذج. وباعتبارها منصة اختبار اختراق مؤتمتة مدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي، فإن Penligent لا تكتفي بالبحث عن التوقيعات المعروفة؛ بل تتصرف مثل المهاجمين.
عند توجيهها إلى البنية التحتية الخاصة بك، يمكن لنواة Penligent العميلة:
- الاكتشاف الذاتي: تحديد مثيلات n8n المكشوفة ونقاط نهاية خطاف الويب التي قد يفوتها المدققون البشريون.
- الاستغلال الآمن: التحقق من صحة CVE-2026-21858 من خلال محاولة منطق التلاعب بنوع المحتوى بدون الكتابة فوق التكوينات بشكل مدمر، مما يثبت المخاطرة مع عدم وجود وقت تعطل.
- المراقبة المستمرة: على عكس الماسحات الضوئية الثابتة، توفر Penligent ذكاءً "بشرياً في الحلقة" تم التحقق من صحته، مما يضمن بقاء طبقة تنسيق الذكاء الاصطناعي لديك مرنة ضد الموجة التالية من حالات عدم الوصول إلى البيانات.
فكرة أخيرة: يعتمد أمان وكلاء الذكاء الاصطناعي لديك بشكل كامل على أمان الأدوات التي تبنيها. لا تدع طبقة التنسيق الخاصة بك تكون الحلقة الأضعف.
المراجع: