With a CVSS score of 10.0, the “React2Shell” vulnerability has shattered the trust model of the React ecosystem. This article provides a hardcore technical analysis of the exploit, explains why Next.js recently released a dedicated command-line tool named fix-react2shell-next to help developers quickly detect and fix the high-risk “React2Shell” vulnerability (CVE-2025-66478), and explores how AI-driven security platforms like Penligent are evolving to catch these complex logic flaws.

Introduction: The Collapse of Trust in RSC
For the seasoned security engineer, CVE-2025-66478 is not just another dependency update. It represents a fundamental breakdown in the architecture of React Server Components (RSC).
The vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code simply by sending a crafted binary stream to the server. The framework blindly deserializes this stream before validating authorization. In response to this critical threat, Next.js recently released a dedicated command-line tool named fix-react2shell-next to help developers quickly detect and fix the high-risk “React2Shell” vulnerability (CVE-2025-66478). Understanding this tool is essential for any rapid response security strategy.
Tactical Response: Deconstructing fix-react2shell-next
Vercel didn’t just release a patch; they released an automated remediation agent. In complex monorepo environments, manually hunting down every vulnerable version of react-server-dom-webpack is a recipe for disaster. The fix-react2shell-next tool is designed to surgically repair the dependency tree.
How the Tool Works
When you execute npx fix-react2shell-next, the tool performs a multi-stage operation:
- Recursive Dependency Scanning: It does not stop at the root
package.json. It traverses the entirenode_modulestree to identify nested dependencies that might rely on vulnerable versions of the RSC renderer. - Deterministic Version Locking: It enforces a strict upgrade path:
- Next.js 15.x is bumped to 15.1.9+.
- Next.js 16.x is bumped to 16.0.7+.
- It also refreshes the lockfile (
package-lock.jsonorpnpm-lock.yaml) to ensure these changes are immutable.
- Canary Resolution: It automatically maps unstable Canary builds to their nearest secure stable counterparts, preventing build breakages during the emergency patch window.
Usage Scenarios
Bash
`# Interactive Mode (Recommended for first run) npx fix-react2shell-next
CI/CD Automated Mode (Force fix without prompts)
npx fix-react2shell-next –fix –json
Audit Mode (Check without modifying)
npx fix-react2shell-next –dry-run`
Anatomy of the Vulnerability: The Deserialization Trap
To understand the severity, we must look at the wire protocol. CVE-2025-66478 exploits the React Flight Protocol—the binary format used for server-client communication.
The Malicious Payload
The flaw lies in how the server deserializes “Module References.” An attacker can craft a payload using the $@ identifier to reference internal Node.js modules that should never be exposed.
Conceptual Exploit Structure:
HTTP
`POST /page HTTP/1.1 Next-Action: a9fa42b4… Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=—-WebKitFormBoundary
——WebKitFormBoundary Content-Disposition: form-data; name=”1_action_arg”
{“$@1”:[“$@2”,null,{“filepath”:”child_process”,”name”:”exec”}]} // The server attempts to “hydrate” this object, executing the exec function ——WebKitFormBoundary–`
Because this deserialization happens before the application logic runs, authentication middleware (like NextAuth.js) is often bypassed entirely.
Why Traditional Security Tools Failed
Legacy security tools were blind to this attack vector.
- WAF Blindness: Most WAFs treat
multipart/form-dataas file uploads. They scan for SQL keywords or script tags, but they do not understand the binary grammar of RSC. A valid Flight payload, even a malicious one, looks like benign data to a regex engine. - DAST Failure: Legacy scanners (DAST) rely on crawling links. Next.js Server Actions use hashed identifiers (e.g.,
a9fa42b4...) which are not exposed as standard URLs. Scanners simply cannot find the entry points.
The AI Security Frontier: Penligent.ai
This failure of legacy tools highlights the necessity of Agentic AI Security. Platforms like Penligent.ai represent the next generation of defense, capable of “thinking” like an attacker.
Context-Aware Reconnaissance
Unlike a dumb scanner, Penligent’s AI agents parse the client-side JavaScript bundles (Source Maps). They extract the hidden Server Action ID maps, effectively reverse-engineering the application’s API surface area in seconds. This allows Penligent to test endpoints that no other scanner can even see.
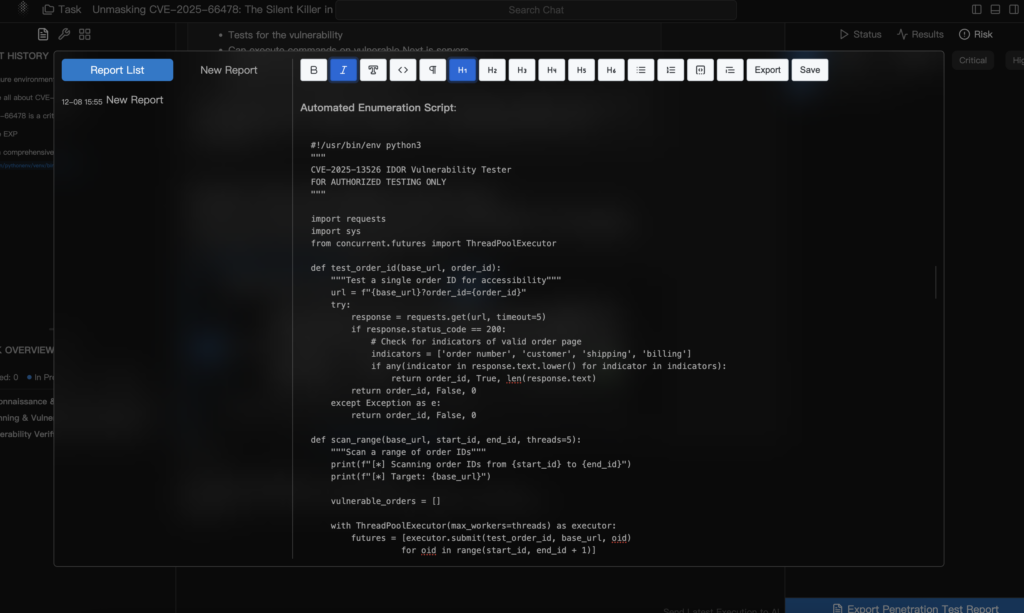
Protocol-Native Exploitation
Penligent understands the syntax of the React Flight protocol. It constructs sophisticated payloads that are syntactically valid but semantically malicious.
Scenario: Penligent identifies a “Update User” action. It crafts a request that is 99% valid but injects a prototype pollution gadget into a nested object property. The server accepts the request structure, triggering the vulnerability deep within the logic flow.
Automated Logic Verification
Penligent validates the vulnerability without crashing the server. It uses Out-of-Band (OOB) techniques, forcing the server to issue a DNS request to a controlled endpoint. This provides 100% certainty of RCE without the risk of false positives common in traditional tools.
Conclusion & Remediation
CVE-2025-66478 serves as a wake-up call. As we abstract away server complexity with frameworks like Next.js, we introduce new, opaque attack surfaces.
Immediate Action Plan:
- Execute the Tool: Run
npx fix-react2shell-nextimmediately across your entire fleet. - Secret Rotation: Assume your environment variables have been compromised. Rotate AWS keys, database passwords, and API tokens immediately.
- Modernize Testing: Move beyond static scanning. Integrate AI-driven penetration testing like Penligent to detect logic flaws that traditional tools miss.
In the age of AI-generated code, security must be equally intelligent.
Recommended High-Authority Resources:


