On January 26, 2026, the cybersecurity landscape was hit with an out-of-band emergency update from Microsoft, addressing CVE-2026-21509. This vulnerability is not just another bug; it is an active zero-day exploit targeting the fundamental way Microsoft Office handles Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) security decisions.
For the rigorous security engineer, understanding the “how” and “why” is more critical than just knowing the KB number. This article provides a technical breakdown, actionable remediation code, and strategies for automated verification.

Technical Deep Dive: The Mechanics of the Bypass
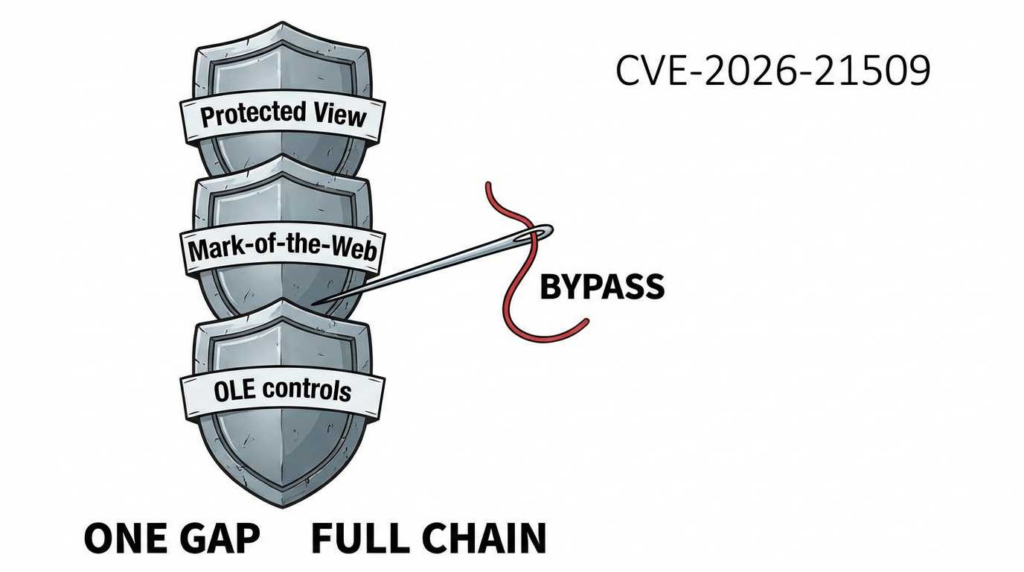
CVE-2026-21509 is classified as a Security Feature Bypass with a CVSS score of 7.8. The critical aspect of this vulnerability is its ability to neutralize the defenses built into the Office suite designed to block malicious COM controls.
The CWE-807 Flaw
הפגיעות נובעת מ CWE-807: Reliance on Untrusted Inputs in a Security Decision. Modern Office applications have layers of “Killbits” and “Protected Views” to stop legacy or dangerous ActiveX/COM objects from initializing.
However, in CVE-2026-21509, the exploit relies on:
- Crafted Metadata: The attacker manipulates the file structure (header information) of an Office document.
- Decision Logic Failure: The Office parser reads this manipulated data and incorrectly determines that the embedded content is “Safe for Initialization.”
- Local Context Execution: Once the check is bypassed, the malicious object loads within the user’s local context. While not a direct Remote Code Execution (RCE) on its own, it removes the only barrier preventing RCE payloads embedded in the document from executing.
Hardcore Mitigation: Registry Intervention
While Microsoft suggests applying the latest patches immediately, sophisticated IT environments require defense-in-depth. Community analysis and reverse engineering have identified specific COM CLSIDs associated with the active exploitation.
The PowerShell Remediation Script
To immediately mitigate the risk before a full patch rollout is complete, you can enforce the “Killbit” via the registry. The following script sets the Compatibility Flags for the vulnerable component {EAB22AC3-30C1-11CF-A7EB-0000C05BAE0B}.
PowerShell
`# CVE-2026-21509 Mitigation Script
Enforces strict COM Compatibility Flags to prevent bypass
$TargetCLSID = “{EAB22AC3-30C1-11CF-A7EB-0000C05BAE0B}” $BaseKeys = @( “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Office\Common\COM Compatibility”, “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Office\Common\COM Compatibility” )
foreach ($Key in $BaseKeys) { $FullPath = “$Key\$TargetCLSID” try { if (-not (Test-Path $FullPath)) { New-Item -Path $FullPath -Force | Out-Null Write-Host “Created key: $FullPath” -ForegroundColor Green } # Setting value to 0x400 (1024) effectively disables the control New-ItemProperty -Path $FullPath -Name “Compatibility Flags” -Value 1024 -PropertyType DWORD -Force | Out-Null Write-Host “Secured: $FullPath” -ForegroundColor Green } catch { Write-Error “Failed to secure $FullPath” } }`
Note: Always test registry changes in a staging environment first. A restart of Office applications is required.
Validating Defenses with AI-Driven Penetration Testing
Patching is only the first step. Verification is the final step. In 2026, manual verification of client-side vulnerabilities across thousands of endpoints is impossible.
Integrating with Penligent.ai
זה המקום שבו Penligent (https://penligent.ai/) transforms the vulnerability management lifecycle. Penligent is an autonomous AI penetration testing platform designed to think like an attacker.
For a vulnerability like CVE-2026-21509, Penligent offers distinct advantages over static scanners:
- Behavioral Validation: Instead of just checking for the presence of a patch (which can be spoofed or fail to apply correctly), Penligent’s agents can deploy harmless test vectors that attempt to exercise the OLE bypass logic.
- Context-Aware Phishing Simulations: Since this CVE requires user interaction, Penligent can automate a simulated phishing campaign. It measures not just the technical vulnerability, but the “Human Firewalls”—tracking how many users open the crafted document and whether the endpoint protection (EDR/ASR rules) successfully blocks the exploitation attempt.
- Continuous Assurance: Penligent runs continuously. If a configuration drift occurs (e.g., a GPO update accidentally reverts the registry fix), Penligent will detect the re-opened vulnerability in real-time.
סיכום
CVE-2026-21509 serves as a stark reminder that legacy technologies like COM and OLE remain relevant attack vectors. By combining rapid registry-level mitigation with intelligent, automated verification tools, security teams can stay ahead of the active exploitation curve.
References & Authority Links: