In the grand timeline of web security, CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) and XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) are the primordial titans. While modern frameworks like React and browser mechanisms like SameSite cookies have dulled their edges in standard web apps, the explosion of בינה מלאכותית סוכנתית ו Microservice Orchestration in 2025-2026 has given these vulnerabilities a terrifying renaissance.
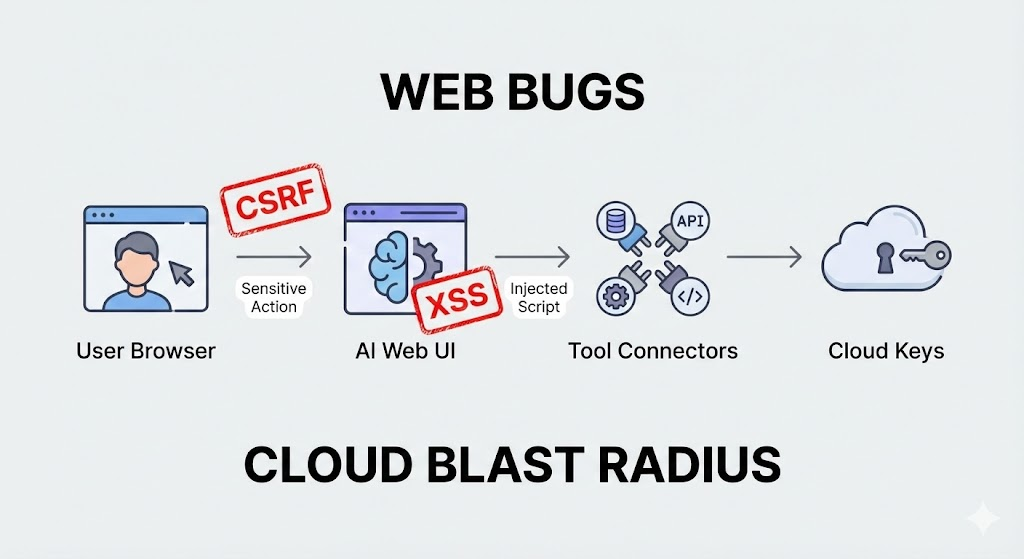
If you are a security engineer architecting infrastructure for LLMs, searching for csrf vs xss isn’t about refreshing your memory on definitions. It is about answering a critical question: When my AI Agent has root-level API access, what is the blast radius of these vulnerabilities?
This guide discards the bootcamp-level explanations. We will dissect the protocol-level differences, the collapse of trust boundaries, and the new exploitation chains targeting AI workflows, concluding with how automated validation platforms like Penligent are essential for survival.
The Fundamental Collapse of Trust
להבין csrf vs xss at an engineering level, we must strip away the syntax and look at the “Direction of Trust.”
XSS: The Betrayal of Content
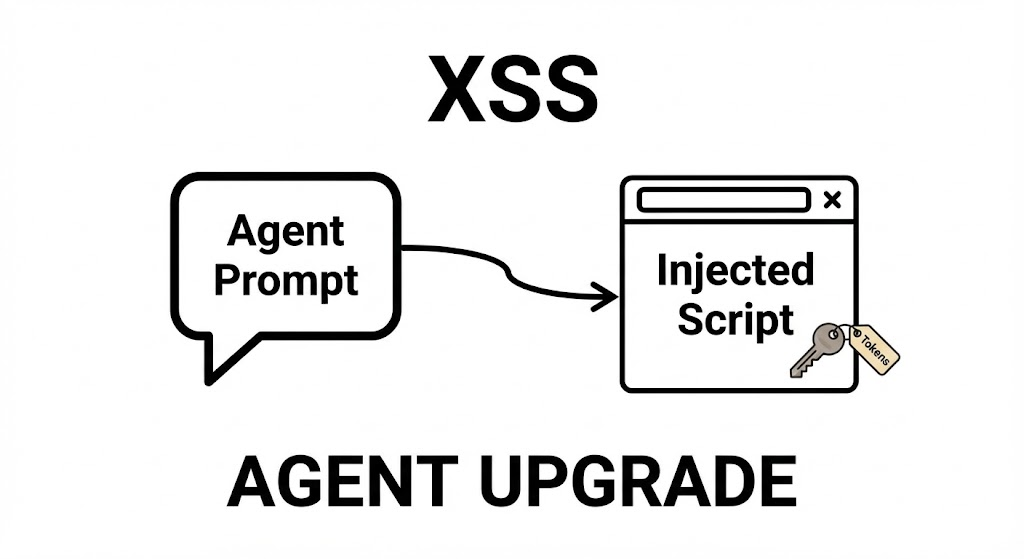
XSS is fundamentally an issue of Context Confusion.
- הוקטור: An attacker injects malicious scripts into regions where the browser expects data (user comments, URL parameters, or crucially, AI-generated Markdown).
- The Trust Failure: The browser cannot distinguish between the legitimate developer’s script and the attacker’s injected script. Because the script executes within the מקור of the application, it inherits all privileges: reading
אחסון מקומי, accessing the DOM, and makingfetch()requests. - AI Era Variant: Prompt-to-XSS. Attackers use Prompt Injection to force an LLM to output unsanitized HTML/JS. If your chatbot interface renders this raw output, you have a Stored XSS vulnerability generated by the AI itself.
CSRF: The Betrayal of Sessions
CSRF is fundamentally an issue of Session Abuse.
- הוקטור: An attacker forces a victim’s browser to send a request to a vulnerable backend where the victim is authenticated.
- The Trust Failure: The server cannot distinguish between a request initiated by the user clicking a button and a request initiated by a hidden form in a malicious iframe. The server trusts the Cookie, and the browser attaches that cookie automatically to cross-site requests (under specific conditions).
- AI Era Variant: Localhost Drive-by. AI engineers run powerful tools (Langflow, ComfyUI, MLflow) on
localhost:7860או127.0.0.1:5000without authentication. A malicious website can fire CSRF requests atlocalhost, effectively bridging the air-gap between the public internet and your private development environment.
The Engineering Comparison Matrix
| תכונה | XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) | CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) |
|---|---|---|
| זרימת נתונים | Bi-Directional (Read/Write). The script runs in the victim’s browser context. It can read API responses, steal tokens, and exfiltrate data. | Uni-Directional (Write-Only). The attacker sends a request but cannot see the response (due to Same-Origin Policy), unless chained with other bugs. |
| Bypass Mechanic | Defeats CSRF Tokens. An XSS payload can simply read the CSRF token from the DOM and include it in its malicious requests. | Defeats Firewalls. CSRF uses the victim’s browser as a proxy to hit internal IPs (Intranet CSRF) that are not accessible from the outside. |
| יעד עיקרי | Identity. Stealing Session IDs, Access Tokens, PII. | State. Changing passwords, deleting workflows, modifying model weights. |
| AI Criticality | גבוה. Can steal the API keys used by the AI Agent to access cloud resources. | קריטי. Can reconfigure the Agent to send all future data to an attacker-controlled endpoint. |
The JSON CSRF Myth & Advanced Vectors
Among senior engineers, misconceptions about CSRF persist. These myths are the cracks where attackers slip through.
Myth 1: “My API is JSON-only, so I am immune to CSRF.”
This is dangerously false.
- The Theory: HTML
<form>tags can only sendapplication/x-www-form-urlencoded,multipart/form-data, אוtext/plain. They cannot natively sendיישום/json. - The Reality:
- CORS Misconfiguration: If your server allows
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *עםAccess-Control-Allow-Credentials: true(a common dev mistake), CSRF is trivial via JS. - Lax Content-Type: Many backends (like older Express.js or Flask apps) will parse a JSON body even if the
סוג תוכןheader istext/plain. - Flash/PDF (Legacy but relevant): Historically, these plugins could send JSON.
- CORS Misconfiguration: If your server allows
The “Fake JSON” Attack:
An attacker can create a form that sends valid JSON syntax as the body, but with a text/plain content type. If your API parses the body without strictly validating the header, you are vulnerable.
HTML
<form action="<https://api.company.com/delete>" method="post" enctype="text/plain"> <input name='{"id": 1337, "ignore": "' value='test"}' type='hidden'> <input type="submit"> </form>

Myth 2: “SameSite=Lax fixes everything.”
בעוד SameSite=Lax is a great default, it is not a silver bullet.
- The 2-Minute Window: Some browsers (like Chrome) implemented a feature where cookies without a SameSite attribute are treated as
רפהbut allow POST requests for 2 minutes after creation (to support login flows). - GET CSRF:
רפהcookies are sent on top-level navigations using GET. If your API violates REST principles and allows state changes via GET (e.g.,/api/destroy_agent?id=1), you are vulnerable.
Case Study – CVE-2025-34291 (Langflow RCE)
To ground this in reality, let’s analyze CVE-2025-34291. This vulnerability in Langflow (a visual AI framework) demonstrates the modern “CSRF to RCE” pipeline.
The Setup
Langflow allows users to upload “Custom Components” (Python scripts) to process data. The API endpoint for this was meant for local use but was exposed on the network interface.
The Exploit Chain
- גילוי: The attacker identifies that Langflow runs on
0.0.0.0:7860in many Docker deployments. - המטען: A Python script containing a malicious payload (e.g.,
os.system('rm -rf /')) embedded in a component definition. - The CSRF: The attacker hosts a “Dark Mode Theme for Langflow” website. Hidden in the background is a script that POSTs the malicious component to
http://localhost:7860/api/v1/components. - The Trigger: A developer visits the theme site. Their browser sends the request to their local Langflow instance.
- ההשפעה: Langflow accepts the request (no CSRF token), loads the component, and executes the Python code. The developer’s machine is compromised.
The Lesson: In AI tools, RCE is often just one CSRF away.
Automated Defense with Penligent
Manual pentesting cannot keep pace with the deployment velocity of AI agents. You need Logic-Aware Automation.
Penligent.ai is the solution for this specific complexity. Unlike regex-based scanners, Penligent uses Agentic AI to understand the כוונה of your application.
How Penligent Differentiates CSRF vs XSS Testing
- Intelligent CSRF Replay:
- Penligent’s agents parse your API documentation.
- They identify state-changing endpoints.
- The agent systematically attempts to replay valid requests while stripping
מקורheaders, removing custom Auth headers, and manipulatingReferer. - It validates the vulnerability by checking if the state actually changed (e.g., did the user get deleted?), eliminating false positives based solely on HTTP 200 codes.
- Semantic XSS Fuzzing:
- For AI applications, Penligent injects Prompt Injection payloads designed to bypass LLM safety filters and output HTML.
- It uses a headless browser to execute the response, verifying if
alert(document.domain)or data exfiltration actually occurs.
- Localhost/Intranet Simulation:
- Penligent can simulate “External to Internal” attacks, verifying if your internal dashboards are susceptible to CSRF attacks from the public internet (DNS Rebinding/Drive-by).
The Hardcore Defense Checklist
- Kill the Cookie (for APIs): For API communication, especially in SPA architectures, move to Bearer Tokens (JWT) stored in memory or handled by a secure BFF (Backend-for-Frontend) layer. Browsers do not automatically send custom headers, neutralizing CSRF.
- Strict Content-Type Validation: Your backend must strictly enforce
סוג תוכן: application/json. If the header is missing or wrong, reject the request immediately. This breaks simple form-based CSRF. - Double Submit Cookie Pattern: If you must use cookies, use the Double Submit pattern. The frontend reads a cookie value and sends it as a custom header (
X-CSRF-Token). The backend verifies the cookie matches the header. - Sanitize AI Outputs: Treat all text coming from an LLM as Hostile. Use libraries like DOMPurify before rendering ANY Markdown or HTML from an AI model.
סיכום
In 2026, the battle of csrf vs xss isn’t about protecting a guestbook from spam. It’s about preventing an autonomous AI Agent from being hijacked to wipe your cloud infrastructure.
XSS allows the attacker to become the user. CSRF allows the attacker to control the user.
For the security engineer, understanding this distinction is vital. But implementing a defense that scales requires moving beyond manual checks and embracing automated, logic-driven security platforms like Penligent to continuously validate the integrity of your AI nervous system.
הפניות
- OWASP Cheat Sheet Series: Cross-Site Request Forgery Prevention
- אקדמיית אבטחת האינטרנט של PortSwigger: XSS vs CSRF
- Google Security Blog: SameSite Cookies Explained
- Penligent Whitepaper: Automating Logic Flaw Detection in AI Agents
- BlackHat 2024: The Death of Localhost: CSRF in the Age of AI Development (Hypothetical reference for context)