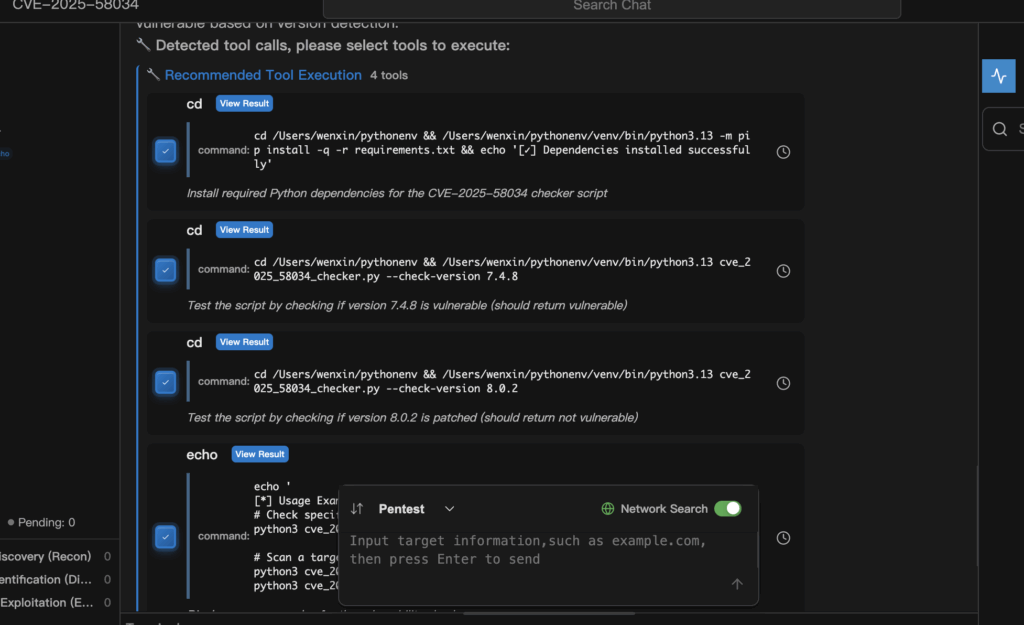
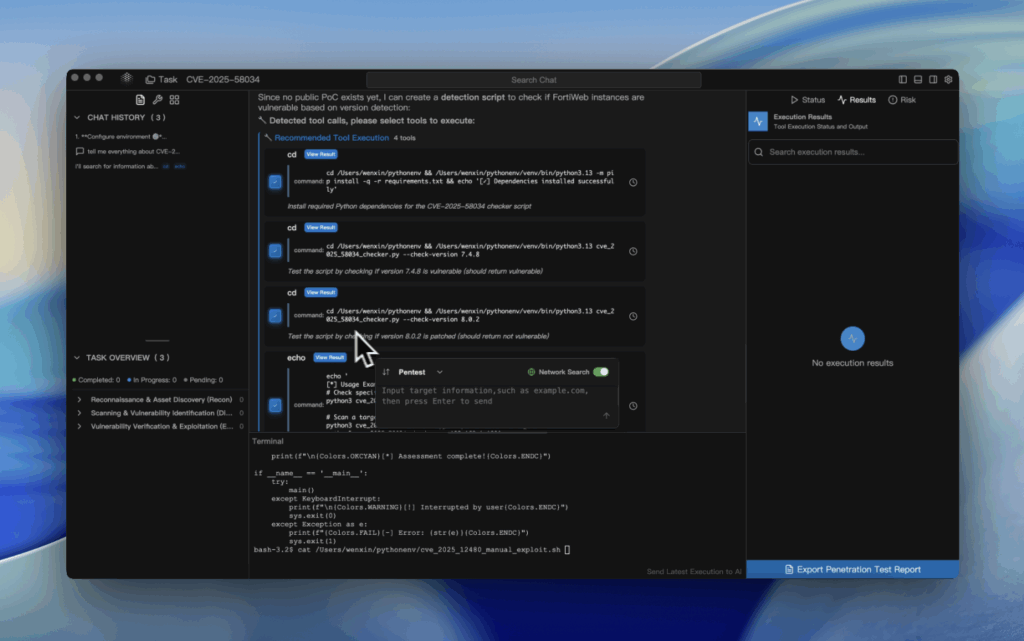
CVE-2025-58034 is an authenticated OS command injection vulnerability (CWE-78) in Fortinet FortiWeb Web Application Firewall (WAF). In affected versions, a logged-in attacker can trigger unauthorized command execution on the underlying system via crafted HTTP management requests or CLI commands. Fortinet has confirmed active exploitation in the wild, and CISA has added this CVE to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, which makes patching urgent even though the base CVSS score is “medium.” (FortiGuard)
FortiWeb appliances sit at the security boundary; once command execution is possible on a WAF, an attacker can disable protections, tamper with policies, and pivot deeper into application networks. That boundary position is why post-authentication RCE on FortiWeb is operationally high-impact despite PR:H in the CVSS vector. (एनवीडी)
Affected and Fixed Versions
Fortinet’s PSIRT advisory and NVD agree on the vulnerable ranges. (FortiGuard)
| FortiWeb Branch | Affected Versions | Fixed Versions |
|---|---|---|
| 8.0.x | 8.0.0 – 8.0.1 | 8.0.2+ |
| 7.6.x | 7.6.0 – 7.6.5 | 7.6.6+ |
| 7.4.x | 7.4.0 – 7.4.10 | 7.4.11+ |
| 7.2.x | 7.2.0 – 7.2.11 | 7.2.12+ |
| 7.0.x | 7.0.0 – 7.0.11 | 7.0.12+ |
There is no reliable workaround publicly recommended beyond removing management exposure and patching, so upgrading is the primary mitigation. (FortiGuard)
Root Cause and Attack Surface
The vulnerability stems from improper neutralization of special elements in OS command context, meaning FortiWeb accepts attacker-controlled input that is later embedded into system-level command execution without adequate escaping. The vendor notes the issue occurs in both API and CLI components, which strongly suggests one or more administrative operations build shell commands by concatenating parameters. (FortiGuard)
Because exploitation requires authentication, the most realistic pathway is: compromise or reuse of admin credentials (weak passwords, shared accounts, exposed management UI, or stolen sessions), followed by command injection to gain full device control. In real incidents, that “post-auth step” is exactly what makes FortiWeb breaches so damaging. (Rapid7)
Severity and Why “Medium” Still Means “Patch Now”
NVD lists CVSS v3.1 as: AV:N/AC:L/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H with a score of 6.7. (एनवीडी)
On paper, PR:H pulls the score down. In practice, two facts override the “medium” label:
- Fortinet states the CVE is actively exploited in the wild. (FortiGuard)
- CISA KEV inclusion signals real attacker value and mandates rapid remediation for U.S. federal systems, usually within days. (सीआईएसए)
So treat CVE-2025-58034 as high priority regardless of the base score.
Defensive Detection
The examples below help you identify exposure without providing an exploit path.
1) Confirm FortiWeb Version (CLI)
# Print system status on FortiWeb CLI
get system status
# Look for: "Version: FortiWeb vX.Y.Z"
2) Passive Version Probe via SSH Banner
"""
Passive FortiWeb version probe by SSH banner.
No attack payloads; safe for authorized inventory checks.
"""
import socket, re
def probe_ssh_banner(host, port=22, timeout=3):
s = socket.socket()
s.settimeout(timeout)
s.connect((host, port))
banner = s.recv(4096).decode(errors="ignore")
s.close()
return banner
def extract_version(text):
m = re.search(r"FortiWeb[-\\s]?v?(\\d+\\.\\d+\\.\\d+)", text, re.I)
return m.group(1) if m else None
host = "YOUR_FORTIWEB_IP"
banner = probe_ssh_banner(host)
ver = extract_version(banner)
print("Banner:", banner.strip())
print("FortiWeb version:", ver or "unknown")
3) Match Against Affected Ranges
"""
Compare detected FortiWeb version against affected ranges.
"""
from packaging import version
AFFECTED = [
("8.0.0", "8.0.1"),
("7.6.0", "7.6.5"),
("7.4.0", "7.4.10"),
("7.2.0", "7.2.11"),
("7.0.0", "7.0.11"),
]
def in_affected_ranges(v: str) -> bool:
v = version.parse(v)
for lo, hi in AFFECTED:
if version.parse(lo) <= v <= version.parse(hi):
return True
return False
test_ver = "7.4.8"
print(test_ver, "affected?", in_affected_ranges(test_ver))
Threat Hunting: What to Look For
Given confirmed in-the-wild exploitation, you should hunt for evidence of credential misuse followed by command execution. Rapid7 and vendor guidance emphasize post-patch log review and config integrity checks. (Rapid7)
Practical signals include:
- New or unusual admin logins (especially from unfamiliar IPs or at odd hours),
- Unexpected management API activity,
- Suspicious child processes spawned by FortiWeb services,
- Policy/config changes that don’t match your change window. (Rapid7)
Example lightweight log triage:
# Search admin login anomalies
grep -Ei "admin|login|cli" /var/log/* 2>/dev/null | tail -n 200
# Look for command-execution style traces
grep -Ei "exec|shell|system\\(|popen|cmd" /var/log/* 2>/dev/null | tail -n 200
If you find credible indicators, treat the appliance as compromised: capture forensics, rotate credentials, and consider rebuild from known-good images.
Mitigation Guidance
Fortinet’s official position is straightforward: upgrade to fixed releases immediately, then validate integrity. (FortiGuard)
In parallel, reduce blast radius by tightening the management plane: limit Web UI / API / SSH access to trusted IP ranges or internal networks, and enforce MFA plus strong credential hygiene. This aligns with the vendor’s best-practice warning that exposed management interfaces increase real-world risk. (TechRadar)
Why CVE-2025-58034 Matters
FortiWeb is meant to be a defensive choke point. When a WAF itself can be driven into command execution by a logged-in attacker, you’ve effectively lost the boundary and handed the attacker a privileged network foothold. With exploitation already observed and KEV status assigned, delay is the enemy here. (Rapid7)
If you manage many customer environments and need to validate versions plus patch priority at scale, a human-in-the-loop automation workflow (e.g., Penligent) can help inventory FortiWeb estates, correlate logs, and produce remediation reports quickly—without turning detection into risky exploit attempts.