Meta description: React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) is a critical pre-authentication RCE affecting React Server Components and Next.js — immediate patching, hardened configurations, edge defenses, and runtime detection are essential. This guide provides threat context, code & CI-safe fixes, and defense-in-depth strategies to secure modern web apps.
What Is React2Shell — And Why Everybody Is Talking About It
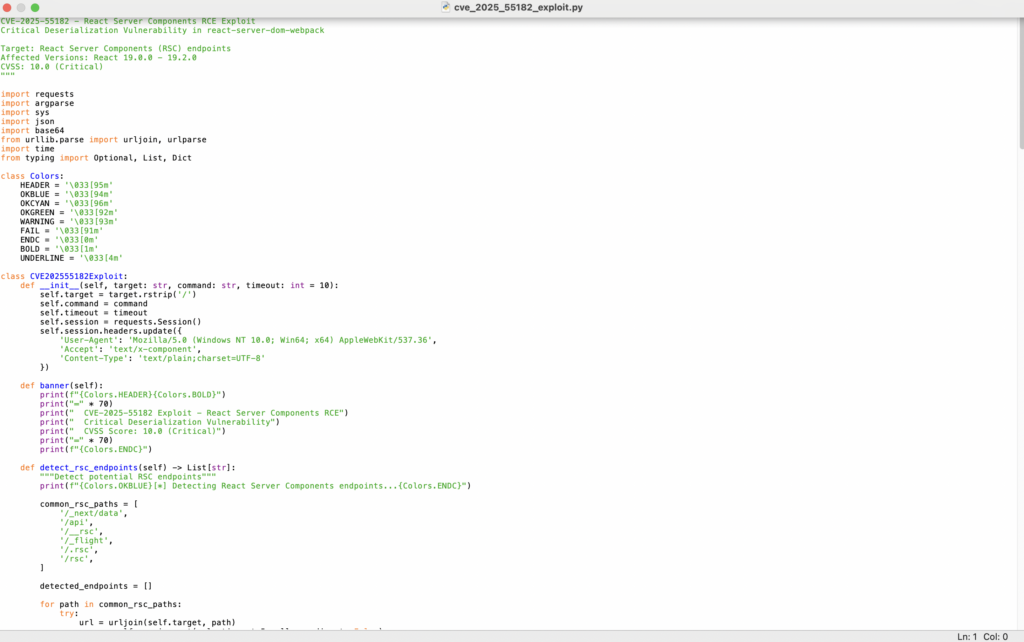
In early December 2025, a critical vulnerability dubbed React2Shell — tracked as CVE-2025-55182 (and alias CVE-2025-66478 for Next.js) — was publicly disclosed. The flaw lies in how the React Server Components (RSC) “Flight” protocol deserializes incoming payloads. An attacker can craft a malicious request and trigger unsafe deserialization on the server, leading to unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE). censys.com+2Sysdig+2
The severity is rated CVSS 10.0 (maximum). NetSPI+1 What makes this especially dangerous is that many default deployments of frameworks like Next.js (with RSC support) become exploitable — even if the developer did not write any custom server-function endpoint. Insight Egnworks+2blog.tecnetone.com+2
Shortly after disclosure, multiple threat intelligence teams and cloud vendors (AWS, GreyNoise, security researchers) reported active exploitation in the wild — including opportunistic scanning, exploitation attempts, and some confirmed intrusions attributed to state-linked groups. TechRadar+3Amazon Web Services, Inc.+3greynoise.io+3
In essence: React2Shell is not theoretical — it’s real, critical, and now.
Who Is Affected — And Who Might Think They’re Safe (But Aren’t)
| Package / Framework | Vulnerable Versions | Patched / Safe Versions (as of Dec 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, react-server-dom-turbopack (RSC core) | 19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0 (react2shell.info) | ≥ 19.0.1, 19.1.2, 19.2.1 (react2shell.info) |
| Next.js (with App Router / RSC enabled) | 15.x, 16.x; certain canary 14.x–14.3.0-canary.77+ (react2shell.info) | 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, 16.0.7 (or later stable) (react2shell.info) |
Important caveat: Even if your application does नहीं define explicit “server-function endpoints,” and even if you think you only use React for client-side rendering, you may still be at risk — because React RSC may be bundled via dependencies, or default scaffolding might include RSC-capable code. unsafe.sh+1
Hence audit carefully — don’t assume “we are safe because we didn’t write server code.”
What Attackers Are Doing Right Now — Real Threats
- Within hours of disclosure, cast widespread internet-scanning campaigns began. greynoise.io+2cyble.com+2
- Some Chinese state-linked APT groups reportedly targeted React2Shell-vulnerable hosts for initial access, then moved to deploy miners, steal credentials, or establish persistence. Amazon Web Services, Inc.+2SOC Prime+2
- Security firms and incident-response teams observed successful exploitation against “vanilla” Next.js apps (scaffolded via
create-next-app) — meaning default setup is no guarantee of safety. blog.tecnetone.com+2byteiota | From Bits to Bytes+2
One community report stands out:
“My NextJS server was compromised by React2Shell exploitation … DDoS abuse notification, 5 distinct malware families deployed, crypto-miner dropper.” Reddit
Given the scale and aggressiveness of attack automation, delayed or superficial response may lead to serious compromises.
Patch Immediately — Using fix-react2shell-next
The fastest, first-line defense is to patch dependencies and rebuild. The package fix-react2shell-next automates detection of vulnerable versions across monorepos and upgrades them. CVE-2025-55182 Scanner+1
Example upgrade command:
दे घुमा के
npx fix-react2shell-next npm install react@^19.2.1 react-dom@^19.2.1 next@^16.0.7
Then rebuild and redeploy, ensuring no old lockfiles or cached packages remain.
Recommended workflow (CI/CD safe):
- Add SBOM or dependency-check step to pipeline.
- Block merges/builds if any vulnerable RSC package remains.
- Clear caches & rebuild entire artifact before deployment.
This ensures your deployment artifacts no longer contain vulnerable code even transitively.
Defense-in-Depth: WAF, Request Hardening & Runtime Detection
Patching removes the bug at source, but robust security demands layered defenses — in case of future misconfig, unknown dependencies, or zero-day variants. Based on public research (e.g. from Sysdig, Wiz, and vendors using Cloud-Native protections) Sysdig+2research.jfrog.com+2, we recommend the following:
Edge-level / WAF protections
Configure or deploy WAF rules to block suspicious POSTs to RSC endpoints (e.g. /_next, /_rsc, or server-function routes), especially if request body size or content-type is unusual (e.g. binary payloads). Many major WAF providers already rolled out React2Shell signatures. Sysdig+1
Request sanitization / body-size limits
If your app includes custom server endpoints, enforce body size limits, restrict content-types, and reject unexpected payloads explicitly. For example (Node/Express style):
जे एस
import { json, urlencoded } from 'body-parser'; app.use(json({ limit: '10kb' })); app.use(urlencoded({ extended: false, limit: '10kb' })); app.use('/api/rsc', (req, res, next) => {if (!['application/json','application/octet-stream'].includes(req.headers['content-type'])) {return res.status(415).end(); }next(); });
This reduces the risk of malformed or malicious payloads triggering the still-complex deserialization logic — buying time until full patching.
Runtime detection / monitoring / process-spawn alerts
Because post-exploit behavior often involves shell spawning (e.g. miners, reverse shells), adding runtime detection (via tools like Falco, runtime-security agents, EDR) helps catch unusual child_process invocations or outbound connections. Sysdig researchers already publicly published detection rules for React2Shell exploitation patterns. Sysdig
Example Hardening: From Patch to Safe Deployment (Code + Configuration)
दे घुमा के
`# 1. Patch dependenciesnpx fix-react2shell-next npm install react@^19.2.1 react-dom@^19.2.1 next@^16.0.7
Clean build environment
rm -rf node_modules .next package-lock.json npm install npm run build

Add SBOM / dependency scan to CI
GitHub Actions snippet`
yaml
name: Prevent React2Shell Exposure on: [pull_request, push]jobs: dependency-check: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v4 - run: npm ci - name: Block RSC packages run: | npm ls react-server-dom-webpack react-server-dom-parcel react-server-dom-turbopack || true npm ls react-server-dom-webpack react-server-dom-parcel react-server-dom-turbopack | grep -E "@(19\\.[0|1])\\." && (echo "Vulnerable RSC found" && exit 1)
Also integrate body-size limits and content-type filtering in your server code as shown above, and deploy a runtime monitoring agent or cloud-native EDR to catch suspicious behavior post-deploy.
Real-World Data: Impact, Exploitation, and Why Delay Is Dangerous
- According to publicly shared telemetry, over 77,000 internet-exposed IPs remain potentially vulnerable. blog.tecnetone.com+1
- Within hours of disclosure, attackers began scanning en masse and exploiting unpatched systems — including attempts by APT groups. Amazon Web Services, Inc.+2SOC Prime+2
- Public proof-of-concept (PoC) code began circulating, and some unpatched hosts reportedly suffered full compromises: malware droppers, crypto-miners, and credential exfiltration. Reddit+1
One Reddit user wrote:
“My NextJS server was compromised by React2Shell … multiple malware families, crypto-miner, credential theft.” Reddit
This is no longer a “patch at convenience” issue — it’s urgent.
कहाँ पेनलिजेंट.ai Fits In — Automated Testing, Continuous Assurance & Regression Protection
For teams using or building security-testing or penetration-testing tools (especially automated or AI-driven), React2Shell illustrates a key lesson: dependency-based vulnerabilities + deserialization risks + default configurations create a massive attack surface.
साथ पेनलिजेंट.ai, you get:
- Automated dependency scanning & SBOM analysis — identify vulnerable RSC packages (react-server-dom-*) or unpatched Next.js versions across multiple repos at once.
- Automated exploitation simulation (safe sandbox) — Penligent’s sandboxed emulation can generate malformed RSC requests (non-destructive), test server response, and detect risky deserialization behavior — without using public PoCs.
- CI/CD integration for regression alerts — if a new pull request reintroduces a vulnerable package or disables security-hardening middleware, पेनलिजेंट.ai triggers alerts before merge.
- Runtime monitoring hooks — integrate lightweight agents or alerting logic to detect process spawning, suspicious outbound connections, or other anomalous behavior (e.g. cryptomining, C2 calls).
In short, using पेनलिजेंट.ai transforms a one-time fix into a continuous security posture, reducing risk even if code changes, dependencies evolve, or human error creeps in.
Best Practices Checklist & Post-Patch Hardening Recommendations
- Patch all RSC and Next.js packages immediately — do not wait for “next sprint”.
- Clean and rebuild artifacts — don’t rely on cached builds.
- Audit dependencies & lockfiles — include transitive dependencies.
- Add CI/CD checks or SBOM enforcement — block merges with vulnerable packages.
- Use WAF or edge-level filtering — block or challenge suspicious Flight-protocol POSTs.
- Sanitize request inputs — enforce body-size limits, content-type whitelisting, JSON schema validation when possible.
- Deploy runtime detection / monitoring — catch process spawning, unusual file or network activity.
- Log, monitor and alert — maintain audit trails for login, deploys, and unusual behavior.
- Treat framework changes as security-critical — even browser-facing packages like React may impact server security when RSC is involved.
- Use automated security tooling (e.g. पेनलिजेंट.ai) — for dependency scanning, regression detection, sandboxed exploit simulation, and security QA.
Final Thoughts
React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182 / 66478) is a watershed event in modern web-app security. It demonstrates that large frameworks — even ones primarily associated with UI rendering — may carry devastating server-side security flaws. For developers, DevOps and security teams: treat this as a zero-day that already went live in thousands of deployments.
Patching dependency versions is only the first, most urgent step. A truly secure posture requires layered defenses: hardening, input sanitization, runtime monitoring, WAF or edge filters, supply-chain auditing, and continuous security testing.
If you’re building, maintaining or auditing web applications, or developing security tooling, now is the time to act before attackers get there. With tools like पेनलिजेंट.ai, you can move from “fire-drill patching” to structured, continuous, automated security assurance — and sleep better at night knowing your app is resilient against React2Shell and future deserialization threats.