For professionals working in cybersecurity and penetration testing, Linux is not merely an optional operating system chosen for convenience, but rather the essential foundation upon which the majority of serious security operations are built. The command line interface, often perceived as daunting for beginners due to its apparent complexity, offers unparalleled efficiency and control for those who master it. Within this environment, tasks ranging from reconnaissance to vulnerability analysis, exploitation of weaknesses, and the automation of entire workflows can be executed with a precision and speed that graphical tools rarely match. In such a context, a Linux Commands Cheat Sheet becomes more than a helpful reference—it serves as an operational asset that can determine whether a test is conducted with efficiency and accuracy or burdened by avoidable delays and missteps.

Why a Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Matters
In the domain of security testing, every second can be critical, and any interruption caused by searching for the correct command syntax or recalling a rarely used parameter can compromise the smooth execution of a task. While extensive manuals and documentation exist, their length and density make them unsuitable for quick reference in high‑pressure scenarios such as live penetration tests, incident response, or forensic analysis. A well‑structured Linux Commands Cheat Sheet distills the essential commands into a concise, easily accessible format, complete with practical variations and examples. This not only reduces cognitive load when switching between tools but also promotes consistency across different test cases, ensuring that tested methodologies remain reliable and repeatable even under tight deadlines.
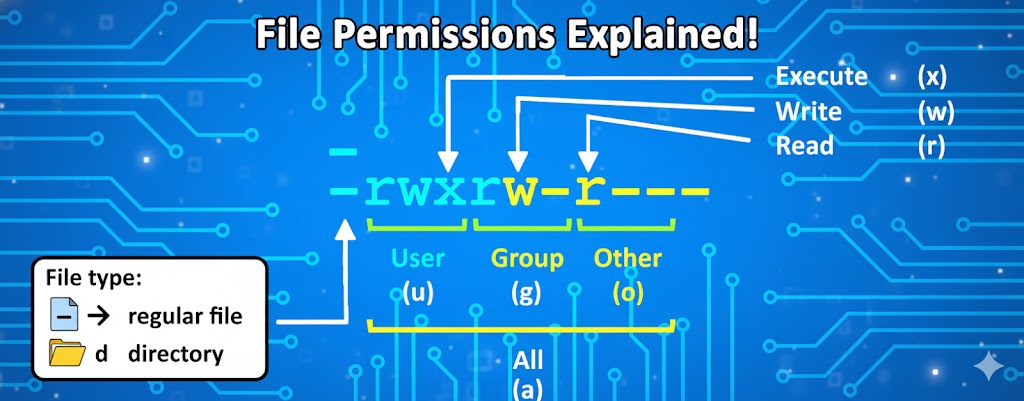
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet: Core Command Categories and Practical Applications
Below is a consolidated table of Linux commands frequently used in cybersecurity and penetration testing. It covers file and directory management, networking, process monitoring, and specialized security tools. Each entry includes a brief description, an example with syntax, and a typical use case so that you can quickly identify when and how to apply it.
| Command | Purpose | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| ls | Lists directory contents | bash\\nls -la\\n | View all files in the current directory, including hidden ones, to examine file system structures. |
| cd | Changes directory | bash\\ncd /usr/share\\n | Navigate quickly to target directories, such as those containing security tools or configuration files. |
| pwd | Prints working directory | bash\\npwd\\n | Confirm your current path, especially important when working within deep nested directories during forensic analysis. |
| ifconfig / ip a | Displays network interfaces | bash\\nip a\\n | Identify available network interfaces and their configurations for environment profiling. |
| ping | Tests connectivity | bash\\nping -c 4 example.com\\n | Verify host availability, useful in preliminary reconnaissance. |
| nmap | Scans networks | bash\\nnmap -sV -A target.com\\n | Discover open ports and service versions to inform later vulnerability assessment. |
| top | Monitors system resources | bash\\ntop\\n | Observe CPU and memory usage in real time to spot abnormal resource consumption. |
| lsof | Lists open files | bash\\nlsof -i :80\\n | Identify processes listening on specific ports for network activity analysis or malware detection. |
| sqlmap | Detects SQL injection | bash\\nsqlmap -u "<http://example.com/page.php?id=1>" --dbs\\n | Automate SQL injection detection and exploitation to retrieve database information. |
| hydra | Brute‑force login | bash\\nhydra -l admin -P passwords.txt ssh://192.168.1.10\\n | Test login credentials against services like SSH, FTP, and HTTP. |
| metasploit (msfconsole) | Exploitation framework | bash\\nmsfconsole\\n | Employ multiple exploit modules from reconnaissance to post‑exploitation. |
| bash scripting | Automates tasks | bash\\nfor ip in $(cat ips.txt); do nmap -sV $ip; done\\n | Execute batch scan tasks to boost efficiency and reduce manual work. |
Batch Scanning Example
#!/bin/bash
targets="ips.txt"
output_dir="scan_results"
mkdir -p "$output_dir"
while read ip; do
echo "[*] Scanning $ip..."
nmap -sV -A "$ip" -oN "$output_dir/$ip.txt"
done < "$targets"
This script reads IP addresses from ips.txt, runs a service scan on each, and stores individual results in the scan_results directory for later review.
Building Efficient Security Workflows with the Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
The strength of this cheat sheet lies not only in knowing each command individually, but in combining them into tailored workflows that match the specific objective of the security task at hand. For example, beginning with a broad scan to map services can be immediately followed by filtering commands to focus only on high‑priority targets, which in turn can be fed into exploitation tools for further testing—all without breaking the operational flow. This chaining transforms isolated commands into a logical sequence that minimizes wasted effort and maximizes useful outputs.
Scaling Security Operations with Bash and the Linux Commands Cheat Sheet
When the scope extends to dozens or hundreds of assets, automation scripting ceases to be a luxury and becomes a fundamental necessity. By embedding commands into Bash loops and scheduled jobs, security teams can enforce standardized scanning procedures, capture output in timestamped logs, and maintain comprehensive historical records without manually repeating the same steps. This approach not only saves time but also guarantees reproducibility, ensuring that verification and follow‑up analyses can reference consistent datasets.
Integrating Penligent with Your Linux Commands Cheat Sheet for Intelligent Testing
Even seasoned security professionals fluent in these commands may find themselves overwhelmed when coordinating multiple tools, validating numerous results, and compiling polished reports under tight deadlines. Penligent addresses this bottleneck by integrating more than 200 security tools into an AI‑driven platform that interprets natural language instructions. A user might simply say, “Check this application for SQL injection vulnerabilities,” and Penligent will select the appropriate tools, run the necessary scans, analyze the results, remove false positives, rank confirmed findings by severity, and produce a ready‑to‑share report complete with remediation guidance. This transforms traditionally resource‑heavy processes into streamlined, intelligent workflows that maintain accuracy while expanding accessibility to team members without command‑line expertise.
Conclusion
A Linux Commands Cheat Sheet is much more than a list—it is a bridge between deep technical knowledge and practical, efficient execution. By combining the precision and flexibility of command‑line mastery with intelligent platforms like Penligent, security professionals can meet the evolving demands of modern testing environments, where speed, accuracy, and adaptability are all non‑negotiable. This synergy of human skill and machine efficiency enables operations to remain both rigorous and agile, delivering stronger security outcomes in less time.


