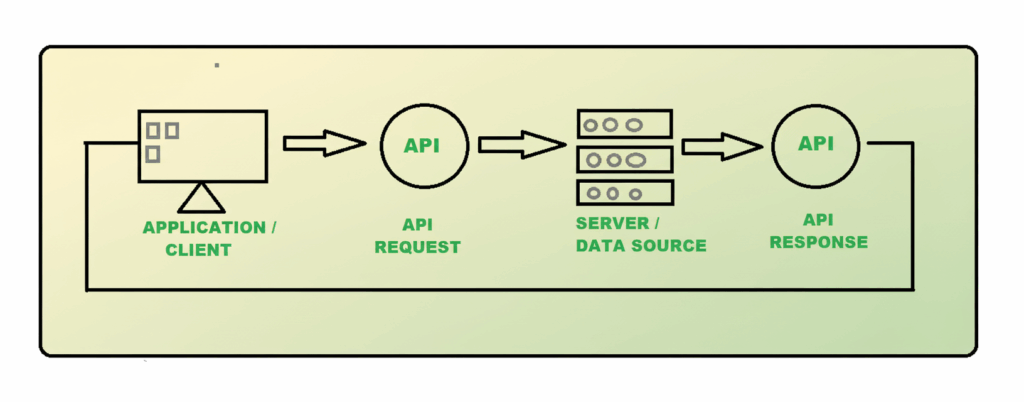
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of modern software systems, enabling communication between applications. However, as these interfaces become more widely used, they also become a target for cyberattacks. API testing is not just a routine quality check during development—it plays a crucial role in maintaining the security of your system.
This guide will walk you through what API testing is, why it matters, the risks involved, and the best practices to keep your API secure and efficient. We’ll look at both functional testing and security measures, ensuring your API meets the highest standards.
What is API Testing?
API testing refers to the process of verifying the functionality, performance, and security of an API, ensuring that APIs do more than just return data correctly—they must also be secure against potential vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, data leakage, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Types of APIs and Priorities in Testing
Not all APIs are the same, and different types have varying levels of security needs and testing priorities:
| API Type | Characteristics | Testing Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Open API | Publicly accessible, minimal or no authentication required | High Security Priority |
| Internal API | Used within internal systems for communication | Medium Security Priority |
| Partner API | Only accessible by specific partners | High Security & Compliance |
| Composite API | Combines multiple APIs, more complex in structure | High Functionality Priority |
Key Goals of API Testing
Functional Accuracy
First and foremost, it’s vital to verify that the API responds correctly to valid inputs and provides the expected outputs, which includes checking HTTP status codes, response data format, and data consistency with the API documentation.
Security Validation
Security is also a critical element of API testing, involving key aspects such as authentication methods (API keys, OAuth, JWT), data encryption and secure transmission using HTTPS, and protection against common attacks including SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Performance and Reliability
APIs must be able to handle high traffic loads, and testing should simulate heavy usage to ensure they perform well under stress. It is also important to verify that rate limiting is in place to prevent abuse and that response times remain acceptable under load.
The API Testing Process
Test Preparation
Before diving into testing, it is essential to review the API documentation, set up a proper testing environment, and gather all necessary credentials such as tokens and API keys to ensure the testing process runs smoothly.
Functional Testing Example
Tools like Postman or cURL are commonly used for API testing. Here’s how you can test an API with cURL:
# Sending a GET request using cURL
curl -X GET "<https://api.example.com/v1/user/123>" \\\\
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \\\\
-H "Accept: application/json"
When testing an API, it is important to ensure that it returns the correct HTTP status codes such as 200, 404, and 500, verify that the structure of the returned data matches the expected format, and make sure that any error messages are user-friendly while avoiding exposure of internal information.
Security Testing Example
SQL Injection Test
import requests
payload = "' OR '1'='1"
url = f"<https://api.example.com/v1/search?q={payload}>"
response = requests.get(url)
if "sql" in response.text.lower() or response.status_code == 500:
print("⚠️ Potential SQL injection vulnerability detected")
else:
print("✅ Input validation passed")
When conducting API testing, make sure that sensitive database error messages are never returned and confirm that query results cannot be manipulated by malicious input.
Common Security Risks in API Testing
When testing APIs, it’s essential to be aware of several common security risks, including weak authentication where APIs have easily guessable keys or passwords, lack of input validation that leaves APIs vulnerable to attacks due to unsanitized inputs, data leakage in which sensitive information is exposed unintentionally, absence of rate limiting that makes APIs susceptible to brute force or denial-of-service attacks, and excessive error exposure where detailed error messages reveal sensitive system information.
Recommended Tools for API Testing
| Tool | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Penligent | AI-powered API security and vulnerability analysis tool | Automated API security testing, threat detection |
| Postman | Comprehensive API testing tool | Functional testing, quick validation |
| OWASP ZAP | Open-source security scanner | Vulnerability detection |
| Burp Suite | Penetration testing toolkit | Advanced security testing |
| JMeter | Load testing and performance | Load testing, stress testing |
| RestAssured | Java-based automation tool | Continuous integration (CI) testing |
Best Practices for API Testing
To ensure that your API testing is as thorough as possible, follow the OWASP API Security Top 10 to mitigate the most common vulnerabilities, use HTTPS and configure TLS encryption to protect data in transit, implement the Principle of Least Privilege by restricting access to only what is necessary, adopt clear versioning strategies for APIs and properly deprecate old versions, integrate automated tests into your CI/CD pipeline for continuous security checks, and perform regular penetration tests and security audits to proactively find and address vulnerabilities.