In the context of cybersecurity, Authn is the abbreviation of “authentication,” and it is far more than a technical process—it is the very first and most crucial barrier in any security architecture. Whether in enterprise-grade internal systems, cloud-based applications, or personal mobile devices, the robustness of authentication often directly determines how hard it is for an attacker to breach the defenses. The core mission of Authn is to confirm the true identity of a user, device, or service, akin to a gatekeeper verifying whether a visitor is truly who they claim to be. For instance, when logging into an online banking service, entering a username and password and passing the check may appear routine, but in fact, it is one of the most critical steps in the overall security chain.

Authn vs. Authz
Although Authn and Authz (authorization) look similar in spelling, they focus on entirely different aspects of security. Authn answers “Who are you?” by ensuring the visitor’s identity matches what the system expects. Authz follows authentication to answer “What are you allowed to do?” by defining permissions. A system might be flawless in Authn, preventing impersonation, yet still be vulnerable in Authz, where missing permission boundaries or logical flaws allow attackers to perform unauthorized operations.
def authenticate(username, password):
valid_users = {"admin": "securePass123"}
if username in valid_users and valid_users[username] == password:
return True
return False
print(authenticate("admin", "securePass123"))# Trueprint(authenticate("admin", "wrongPass"))# False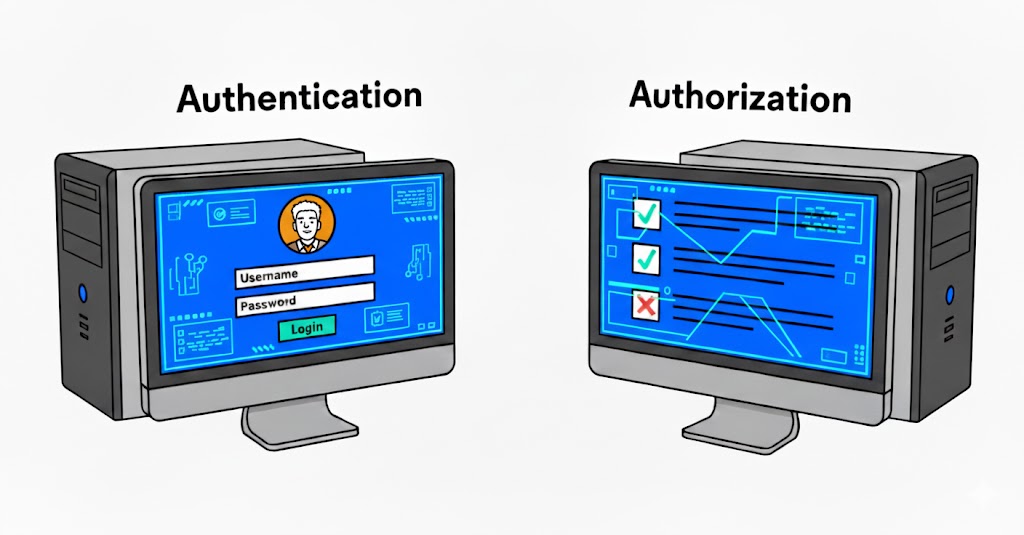
Common Authn Methods
The most familiar method is password-based authentication, which is easy to implement but susceptible to brute-force or credential leakage. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens protection by adding steps such as time-based codes or hardware tokens. For higher-security environments, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) enables certificate-based Authn, almost eliminating the risk of forged credentials. Meanwhile, OAuth and OpenID Connect have gained wide adoption in cross-platform and social logins, simplifying processes while enhancing reliability.
Authn Vulnerabilities and Risks
Authn flaws are high-priority targets during penetration testing because bypassing authentication often means gaining direct access to system resources. For example, if a system allows unlimited login attempts, a brute-force tool can quickly guess valid credentials:
hydra -l admin -P passwords.txt 192.168.1.100 http-post-form \\
"/login:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^:F=incorrect"
Weak password policies, token exposure, and session fixation are other frequent risk points.
Impact of Modern Security Architectures
PKI application strengthens Authn by making credential forgery extremely difficult. The zero-trust model demands rigorous authentication for every request, eliminating default trust in internal networks and reducing insider threat risks.
Best Practices for Securing Authn
Enhancing Authn security requires a combination of strong password policies, MFA, encrypted transmission, and continuous audit of login events. Yet, static strategies alone cannot address evolving attack methods. Penligent, an AI-powered intelligent penetration testing platform, allows testers to type natural language commands such as “Scan the login module for MFA bypass vulnerabilities,” automatically selects the right tools, verifies vulnerability authenticity, prioritizes risks based on impact, and generates detailed reports with remediation guidance. This transforms Authn defense from reactive patching to proactive, automated discovery and resolution, while dramatically reducing the time needed for vulnerability management.
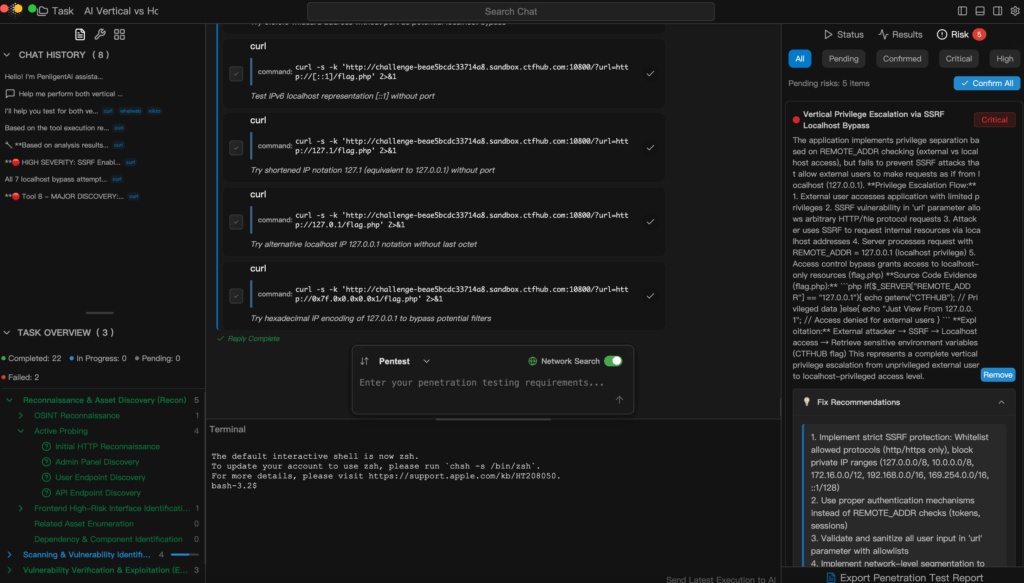
Authn in Threat Intelligence and Tools
In threat intelligence platforms, Authn-related risk data can help trace the origins of attack chains, offering a foundation for defensive measures. Security labs use these vulnerabilities for replication and training, improving understanding of authentication mechanism strengths and weaknesses.
Conclusion
Authn is a foundational element of cybersecurity. Neglecting it can expose organizations to severe consequences. By integrating intelligent penetration testing platforms like Penligent, authentication security can be significantly reinforced, ensuring organizations stay ahead in defending against modern threats.