그리고 인증 토큰 조작 오류 는 종종 다음과 같은 경우에 나타납니다. Linux 사용자 다음과 같은 명령을 사용하여 비밀번호 변경을 시도합니다. passwd. 단순한 운영상의 문제처럼 보일 수 있지만, 보안 연구자와 DevSecOps 엔지니어에게는 이 오류가 잘못 구성된 시스템부터 악용 가능한 취약점까지 인증 워크플로에 더 심각한 문제가 있다는 신호인 경우가 많습니다. 이를 방치하면 권한 상승, 세션 하이재킹, 민감한 데이터 유출에 노출된 환경에 놓일 수 있습니다.

시스템 및 자동화 환경에서의 인증 토큰 조작 오류 원인
| 원인 카테고리 | 특정 원인 | 일반적인 시나리오 예시 |
|---|---|---|
| 시스템 수준 | 잘못 구성된 PAM 모듈 설정 | /etc/pam.d/common-password 잘못된 구성 차단 토큰 업데이트 |
잘못됨 /etc/shadow 권한 | 권한이 0640으로 설정되지 않음 | |
| 루트 파티션 마운트 읽기 전용 | 중요한 인증 파일에 쓸 수 없음 | |
| 디스크 공간이 가득 찼습니다. | 파일 쓰기 작업 실패 | |
| 파일 시스템 오류 | 경미한 부패가 필요한 경우 fsck 수리 | |
| 자동화/CI/CD | 충분한 권한 없이 파이프라인 실행 | 컨테이너 누락 --특권 플래그 |
| 종속 작업이 완료되기 전에 토큰을 지우는 임시 환경 | 프로세스 도중 토큰 제거 | |
| 빌드에서 직접 OS 수준의 비밀번호 조작 | 보안 토큰 처리 원칙 위반 |
인증 토큰 조작 오류 보안 위험
반복되는 토큰 조작 오류는 인증 설계의 시스템적 취약점을 나타내는 위험 신호일 수 있습니다. CI/CD 파이프라인에서 잘못 관리된 토큰은 MITM 공격을 통해 가로채거나 빌드 로그에 노출될 수 있으며, 다음과 같은 민감한 파일에 대한 부적절한 권한이 노출될 수 있습니다. /etc/shadow 를 사용하면 공격자가 비밀번호 해시를 훔쳐 오프라인 크래킹을 시도할 수 있습니다.
운영 및 보안 문제 해결
해결 방법 인증 토큰 조작 오류 근본 원인이 제거되었는지 확인하기 위해 각 수정 사항이 검증을 통해 구현되는 체계적인 프로세스가 효과적으로 필요합니다. 일시적인 잠금 또는 인증 세션 중단이 의심되는 경우 제어된 재부팅을 통해 이러한 일시적인 상태를 제거할 수 있습니다:
sudo 재부팅
잘못 구성된 PAM(플러그형 인증 모듈) 스택이 토큰 업데이트를 방해할 가능성이 있는 경우, 상승된 권한으로 재구성하면 적절한 토큰 처리를 보장할 수 있습니다:
sudo pam-auth-update
루트 파티션이 예기치 않게 읽기 전용 모드로 마운트된 경우 쓰기 권한으로 다시 마운트하면 업데이트 기능이 복원됩니다:
sudo mount -o remount,rw /
다음을 확인합니다. /etc/shadow 보안 권한이 있습니다(0640), 합법적인 액세스와 무단 노출에 대한 보호의 균형을 유지합니다:
sudo chmod 0640 /etc/shadow
다음과 같은 도구를 사용하여 과도한 디스크 사용량을 제거하세요. 블리치비트 또는 FSlint 를 사용하여 쓰기 오류를 방지하세요. 마지막으로, 파일 시스템 손상이 의심되는 경우 영향을 받는 볼륨을 마운트 해제하고 fsck를 클릭하고 중요한 데이터를 백업한 후 프로덕션용으로 다시 마운트하세요:
# 영향을 받는 볼륨 마운트 해제범위 /dev/sdXn 마운트 해제
# 파일 시스템 검사 및 복구 실행도 fsck -f /dev/sdXn
# 중요 데이터 백업유도 tar -cvzf /mnt/backup/critical-data.tar.gz /mnt/production-data
# 프로덕션 용도로 다시 마운트유도 마운트 /dev/sdXn /mnt/production
토큰 보안을 위한 DevSecOps 모범 사례
재발을 방지하기 위해 인증 토큰 조작 오류를 사용하여 DevSecOps 워크플로우의 모든 단계에 보안 토큰 관리를 포함하세요. 해시코프 볼트나 AWS Secrets Manager와 같은 시스템에서 정적 자격 증명을 관리형 비밀로 대체하고, 수명이 짧은 범위의 토큰을 적용하고, 파이프라인에서 OS 수준의 직접적인 비밀번호 조작을 피하고, 실행 전에 자동화된 환경 검사를 수행하세요. 정적 코드 분석을 통해 안전하지 않은 관행을 발견하고 동적 런타임 스캔을 통해 활성 위험을 식별하여 지속적인 토큰 보안을 보장합니다.
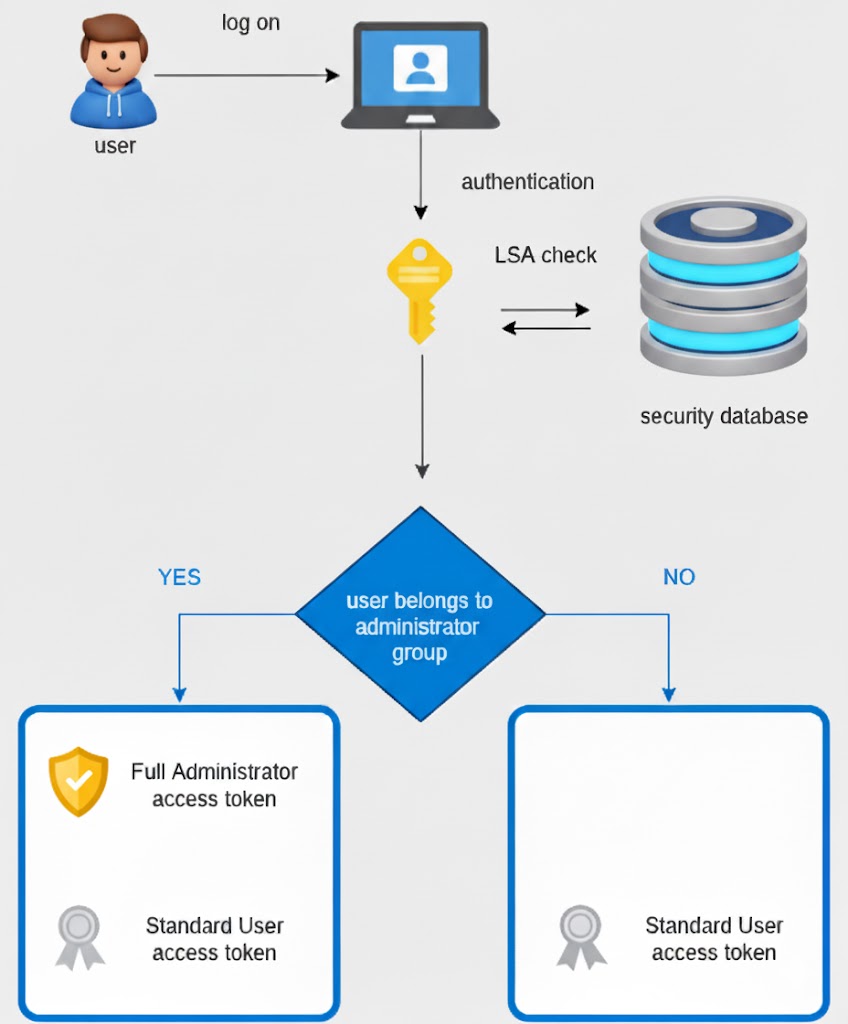
인증 토큰 조작 오류 탐지 및 익스플로잇
언제 인증 토큰 조작 오류 는 인증 흐름에 더 깊은 결함이 있음을 암시하며, Penligent는 탐지 및 수정 작업을 간소화합니다. Nmap, Burp Suite 또는 SQLmap과 같은 도구를 수동으로 연결하는 대신 일반 언어 - 예, "토큰 조작 스캔". 펜리전트는 200개 이상의 통합 도구 중에서 선택하여 타겟 테스트를 실행하고 실제 취약점을 확인하며 오탐을 걸러낸 후 우선 순위가 지정된 수정 보고서를 작성합니다.
결론
그리고 인증 토큰 조작 오류 는 인증에 잠재적인 결함이 있다는 신호이므로 신속하게 해결해야 합니다. 보안 토큰 관행과 자동화된 보안 검사를 Penligent와 같은 도구와 통합하면 탄력적인 인증을 보장하고 침해 위험을 줄일 수 있습니다.


