In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, filter bypass has become a critical concept for penetration testers, vulnerability researchers, and security professionals. It refers to circumventing security filters — such as Web Application Firewalls (WAF), Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), content filters, or antivirus scanners — to allow data or requests that would otherwise be blocked. Used ethically, filter bypass testing helps strengthen defense systems; used maliciously, it can lead to serious security breaches.

Understanding Security Filters
| Filter Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Content Filter | Screens web pages, emails, or messages for malicious keywords, patterns, or prohibited content. |
| Network Filter | Monitors network packets and communication attributes to block suspicious or unauthorized traffic. |
| Antivirus Filter | Scans files for harmful code signatures and isolates detected threats. |
| Web Application Firewall (WAF) | Filters HTTP requests to block SQL injection, XSS, and other web attack patterns. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention System (IDS/IPS) | Detects or blocks malicious activities within a network, often in real time. |
What is Filter Bypass in Cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, Filter Bypass means finding a way to sneak past a security system that is designed to block certain data, files, or network requests — using methods like payload modification, traffic obfuscation, or exploiting filter weaknesses. Think of a security filter like a guard at a checkpoint, if you show something suspicious, the guard stops you. If you disguise it or change how it looks, you might walk past unnoticed.
Filter Bypass is not always bad — ethical hackers and security testers use it to find weak spots and help improve protection. But if abused, it becomes a tool for cybercriminals to steal data, install malware, or damage systems.
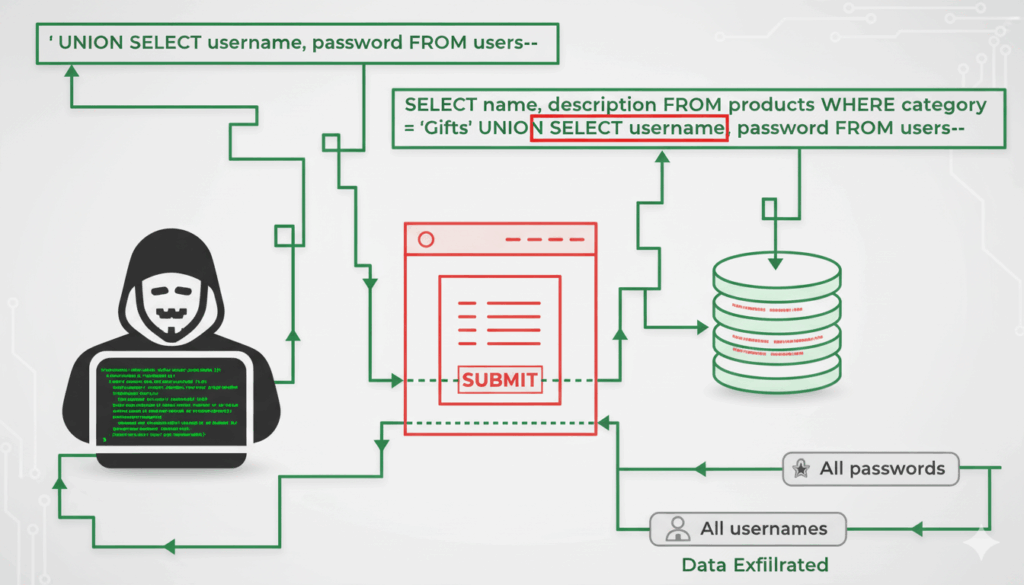
Filter Bypass Techniques & Code Examples
Code Obfuscation & Encoding
Encode payloads (e.g., Unicode, Base64) to evade keyword-based filters.
payload = "<script>alert('XSS')</script>"
obfuscated = ''.join(['\\\\u{:04x}'.format(ord(c)) for c in payload])
print(obfuscated)
Packet Crafting
Modify packet headers, IP addresses, or flags to disguise malicious traffic as legitimate.
from scapy.all import *
packet = IP(src="192.168.1.100", dst="10.0.0.5")/TCP(dport=80)/"GET / HTTP/1.1"
send(packet)
Alternative Ports & Protocol Tunneling
Use non-standard ports or wrap traffic inside another protocol to bypass restrictions.
import socket
s = socket.socket()
s.connect(('target.com', 443))
s.send(b'GET /data HTTP/1.1\\r\\nHost: target.com\\r\\n\\r\\n')
s.close()
File Type Masquerading
Embed malicious code in safe-looking files to evade antivirus detection.
import os
os.rename('malware.exe', 'photo.jpg')
DNS Spoofing / Domain Fronting
Alter DNS records or route through trusted domains to bypass domain-level restrictions.
print("Spoofing DNS to redirect target.com")
Safety Reminder
These examples are for authorized lab environments only. Deploying bypass techniques without permission is illegal in most countries.
How AI Detects Filter Bypass Attacks
AI has revolutionized detection of filter bypass attempts. Unlike static rule-based systems, AI-powered anomaly detection analyzes traffic patterns, behavior anomalies, and payload attributes to identify bypass attempts that traditional filters miss.
Penligent takes this capability further:
- Natural language commands like “Check for WAF evasion attempts” remove the need for scripting or manual tool setup.
- Its AI Agent selects from 200+ integrated security tools (Nmap, SQLmap, Nuclei, etc.), plans and executes adaptive tests.
- Penligent verifies vulnerabilities, removes false positives, and prioritizes threats for efficient mitigation.
- Generates detailed remediation reports instantly, supporting real-time collaboration.
Unlike traditional scanners, Penligent learns continuously, predicting attacker strategies and adapting defenses before new bypass techniques cause damage.
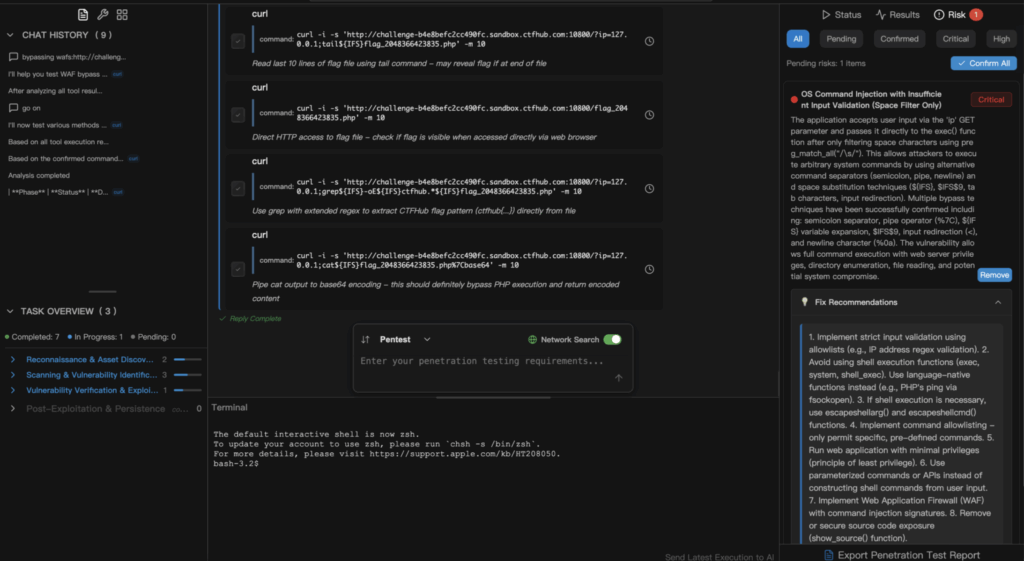
Conclusion
Filter bypass is neutral; its impact depends on intent and authorization. Understanding these methods enables proactive defense against evolving threats. Tools like Penligent make advanced, adaptive security accessible to more teams — turning detection into prevention in today’s AI-powered cybersecurity world.